What is it:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer. It is characterized by the growth of a small tumor that starts as a red spot and slowly grows over time.
BCC is not very aggressive and normally only affects the skin. In most cases, the chances of a cure are high, as most it is possible to surgically remove all cancerous cells, especially if the cancer is diagnosed in its early stages.
This type of cancer is most common after 40 years of age, especially in people with lighter skin, blonde hair and light-colored eyes who expose themselves to excessive sun. Nonetheless, basal cell carcinoma can appear at any age, which is why skin monitoring should be a lifelong habit.
Main symptoms
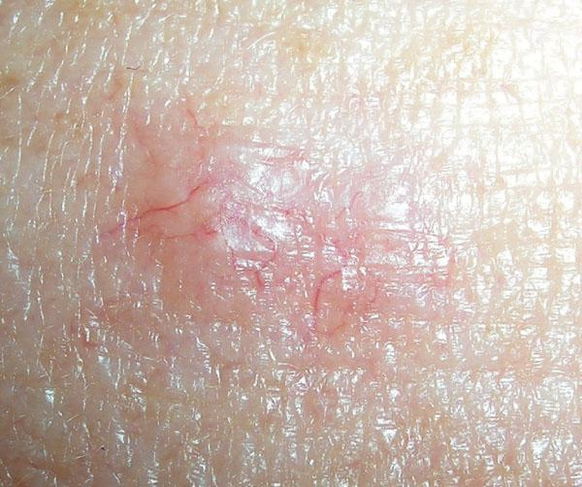
This type of cancer mainly develops on parts of the body that are most exposed to the sun, like the face and neck. Basal cell carcinoma is associated with symptoms like:
- A small wound that never heals and bleed frequently
- A small, elevated white lump on the skin where blood vessels may be noted
- A small brown or red spot on the skin that increases in size over time
These signs should be assessed by a dermatologist if you suspect skin cancer. The doctor may obtain a skin biopsy to remove some of the tissue and evaluate whether malignant cells are present.
If the spot on the skin has very irregular borders, is asymmetrical or grows very quickly over time, it may be a sign of a melanoma. This is a more serious type of skin cancer.
Possible causes
Basal cell carcinoma occurs when cells of the outermost layer of the skin undergo a genetic mutation that causes them to reproduce in an uncoordinated fashion, It leads to the growth of lesions on the body, particularly the face.
The abnormal cell growth is triggered by excessive exposure to UV rays that are emitted by the sun or by tanning beds. However, people who have not been exposed to the sun can still develop BCC. The underlying cause of this type of BCC is not well known.
Types of basal cell carcinoma
There are various types of basal cell carcinoma, which include:
- Nodular basal cell carcinoma: This is the most common type and usually affects the skin on the face. It normally starts as a wound in the middle of a red spot.
- Superficial basal cell carcinoma: This type mainly affects the torso and back, and can be confused with skin erythema or general redness.
- Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma: This is the most aggressive type and can spread to other parts of the body.
- Pigmented basal cell carcinoma: This type is characterized by darker spots and can be difficult to discern from melanoma.
The different types of BCC are differentiated based on their presenting characteristics, which can be similar and difficult to identify. Therefore, if you suspect you may have skin cancer due to the growth of a suspicious spot on your skin, you should see a dermatologist for assessment.
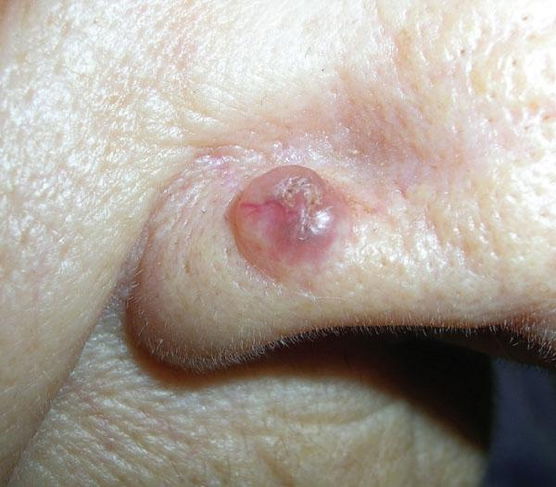
Treatment options
In most cases, treatment is done with laser surgery or cryotherapy to the spots. This helps to eliminate and remove malignant cells, which prevents further spread.
After removal, follow-up appointments with further testing are very important to assess whether the cancer continues to grow or if a full cure has been achieved. Cases of BCC that have resolved should be reevaluated once per year to guarantee the cancer has not returned.
If surgery or cryotherapy is not effective and the cancer continues to grow, radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be necessary to delay the growth and development of malignant cells.
How to prevent BCC
To prevent basal cell carcinoma, you should use sun screen with an SPF over 30. You should also avoid sun exposure during hours of intense U rays, and use hats and clothing with SPF protection. You should generally avoid artificial UV rays and tanning beds.
It is important to be cautious with children and babies, and to apply sun screen with accordance to their age. This population is even susceptible to the negative effects of UV rays.






























