Bumps on the skin can develop in both adults or children. They are generally not a sign of a serious illness, and usually occur due to mild conditions, such as keratosis pilaris, acne, folliculitis or a skin allergy.
Bumps on the skin can also be a sign of a gluten intolerance, especially if the bumps are accompanied by intense itching and gastrointestinal symptoms.
If you notice that you have bumpy skin, you should see a doctor for assessment. The doctor will inspect the bump characteristics and whether they developed in a specific spot on the body. Reporting any other symptoms is helpful for confirming a diagnosis, which will ultimately help to guide treatment.
What causes bumps on the skin?
The most common causes of bumpy skin are:
1. Keratosis pilaris
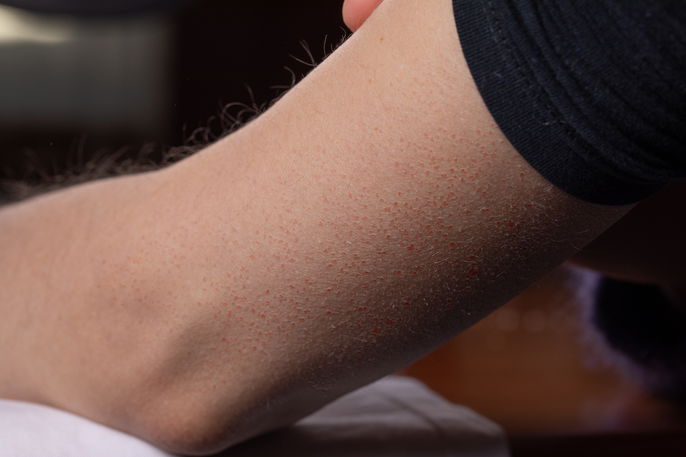
Bumps that appear on the side or back of the arms or bumps that appear on your glutes can appear due to excessive production of keratin in the skin, also known as keratosis pilaris. This change is a genetic characteristic and therefore there is no cure. However, if it is left untreated, the bumps can become inflamed from touching them with dirty hands, leading to darkened skin.
What to do: These bumps tend to appear more often in the summer due to sweat and use of tighter clothing. Therefore, you should opt to use light clothes that allow to the skin to breathe. You should also avoid exfoliating, as this can worsen the bumps. Use moisturizing creams with urea, glycolic acid os salicylic acid as active ingredients to control the production of dead cells and keep the skin hydrated.
2. Acne or pimples
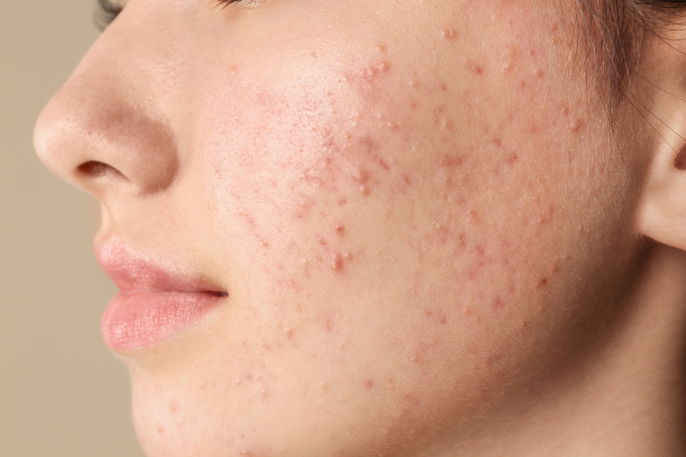
Acne or pimples can appear as red bumps and mostly affect adolescents and young adults. They are more common in the summer and can cause other symptoms like itching, especially with excessive sweating.
What to do: You should use skin products that are aimed at treating acne. You should look for products that control sebum production and manage oiliness to prevent pimples from getting larger or more inflamed. You should avoid squeezing pimples, as this habit can lead to scarring that is difficult to treat.
Check out ways to get rid of acne scars using home remedies or cosmetic procedures.
3. Ingrown hairs
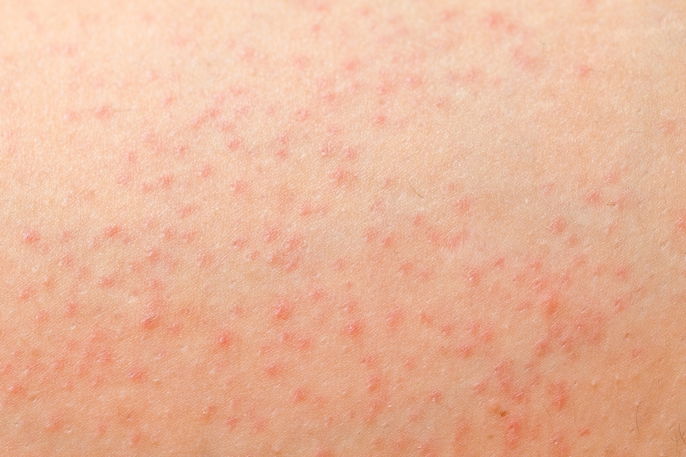
Ingrown hairs, also known as folliculitis, is another common cause of small bumps or lumps in the arms, groin, legs and armpits. They are usually related to shaving, but can also occur due to tight clothing that causes consistent friction against the skin.
What to do: You should exfoliate the skin frequently, especially before hair removal. Looser clothing can also help to prevent ingrown hairs. If you suspect that an ingrown hair has become infected, the doctor may prescribe a topical antibiotic to be applied for 7 to 10 days.
Learn more about ways to get rid of ingrown hairs using home remedies or other cosmetic procedures.
4. Skin reaction
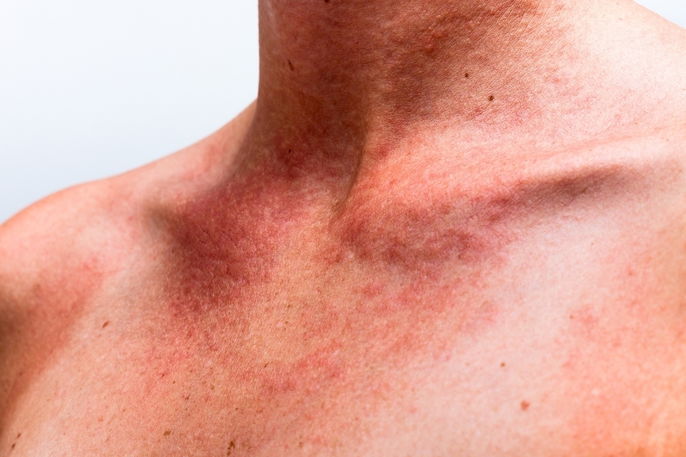
A skin reaction can cause intense itching, which can lead to the formation of small, crusting bumps or wounds. This reaction can occur due to food allergies, animal fur, certain fabrics, cosmetic products or contact with an insect.
What to do: The doctor may recommend treatment with an anti-allergenic, like hydroxizine or cetirizine. You should run the affected skin under water to remove the trigger and soothe the skin. With more severe cases, you should proceed to the emergency room, as injectable medication may be required.
5. Shingles
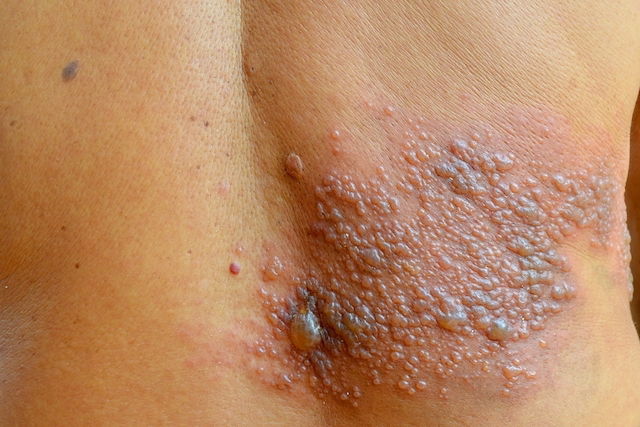
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is caused by the same virus as chicken box. Its main symptom is the appearance of red bumps on the skin, particularly on the chest, back and abdomen. These bumps develop into blisters that are itchy and painful.
What to do: You should be assessed by a doctor if you suspect shingles so that a diagnosis can be confirmed. Treatment is aimed at decreasing virus activity, which is normally done with antivirals.
6. Gluten intolerance
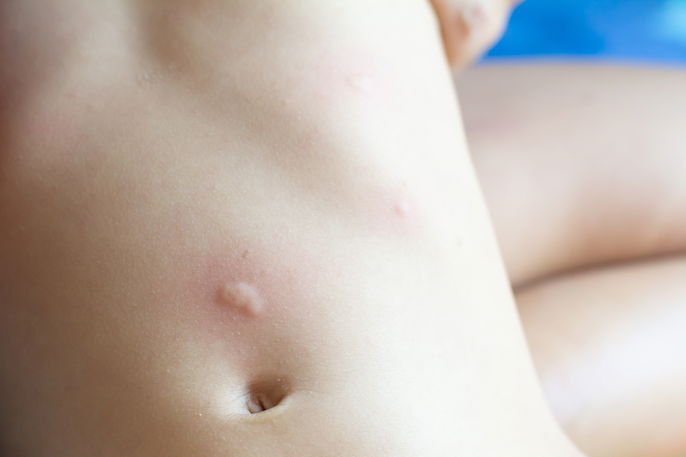
A gluten intolerance usually presents with gastrointestinal symptoms, however dermatitis can also occur. It is common to have small, itchy bumps that burn and then peel to appear after consuming gluten.
Read more about gluten intolerance symptoms and complete our online quiz to determine your risk for this condition.
What to do: The doctor may indicate the use of ointments or creams to relieve skin symptoms, however lifestyle habits will be necessary to prevent future reactions. You should avoid eating food with gluten, like wheat, rye and barley. Check out our list of gluten free food that you can incorporate into your diet instead.
You should see a registered dietitian before embarking on a celiac disease diet to ensure this diet is right for you.
7. Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammation of the skin that can cause dryness, itching, redness and bumps on the skin, especially in the folds of the arms and knees, neck, hands and feet in adults. In babies, it is most commonly affects the cheeks and the skin around the ears.
What to do: Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms. The dermatologist may recommend the use of topicalç corticosteroid or immunosuppressive ointments, such as betamethasone or tacrolimus oral corticosteroids, antihistamines or injections.






























