Cyanosis is the blue or purple discoloration of the skin, nails or lips. It is caused by changes in blood circulation or in the oxygenation of hemoglobin (which is a components of red blood cells). Cyanosis can be caused by exposure to cold, but is often related to illnesses such as heart failure, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
If you notice cyanosis frequently, it should be assessed and treated. the doctor will evaluate your health history, perform a physical assessment and order testing to identify the cause, which will help to guide treatment.
As cyanosis can be a serious condition and therefore you should seek urgent medical attention if you notice it, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain and coughing.
Types of cyanosis
According to the speed, flow of blood circulation and amount of oxygenated blood reaching the organs, cyanosis can be classified into:
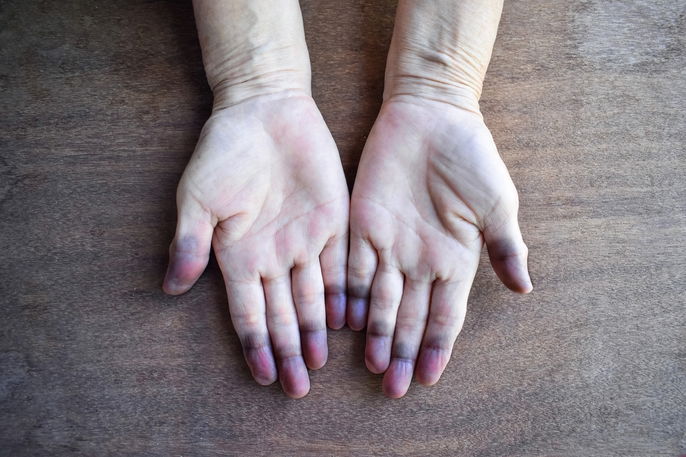
1. Cyanosis in the extremities
Cyanosis in the extremities is usually the result of reduced blood flow and speed to the limbs due to low oxygen levels in the body.
This type of cyanosis, also known as peripheral cyanosis, appears only in the upper and lower extremities of the body, such as the tips of fingers and toes, nails, tip of the nose, ears, tongues, gums and lips.
In addition to a blue or purple color, affected areas may also be colder to the touch and blood pressure may be lower.
2. Central cyanosis
Central cyanosis occurs when blood that is flowing in the arteries has little or no oxygen. This affects all surfaces of the body and mucous membranes, giving them a blue or purple color on the skin. Other symptoms include difficulty breathing and a higher blood pressure.
3. Mixed cyanosis
This type of cyanosis occurs when both the flow and speed of blood circulation are reduced, and the blood that reaches the arteries has little or no oxygen.
Main causes
Cyanosis can be caused by any condition that alters blood oxygenation and transport, and can affect adults and children. The main causes of cyanosis are:
Lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary emphysema or pneumonia;
- Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, atherosclerosis, congenital heart disease and thrombosis
- Beta-blocker medications, used to treat high blood pressure, such as carvedilol, bisoprolol and metoprolol
- Blue baby syndrome, which is a genetic disease characterized by changes in heart function that reduces the amount of oxygen circulating in the body
- Exposure to cold air or cold water, which cause blood vessels to contract and reduces blood circulation to the extremities
- High hemoglobin levels, which can be caused by situations such as dehydration and kidney tumor, leading to other symptoms, such as dizziness and loss of vision, for example.
Cyanosis can also occur with high altitudes, as well as health conditions like polycythemia, generalized infections and Raynaud's syndrome.
Confirming a diagnosis
Cyanosis should be confirmed by a doctor, who generally assesses the person's physical condition and health history. The doctor may also order testing, such as a blood test, X-ray, electrocardiogram, ultrasound and CT scan. These can help to identify the possible cause of cyanosis and guide the most appropriate treatment.
Another test that may be requested by the doctor is an arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, a blood test that assesses the efficiency of oxygen exchange in the blood. It helps to assess lung functioning.
Also recommended: Arterial Blood Gases (ABG's): What It's For & Normal Levels tuasaude.com/en/abg-arterial-blood-gasTreatment options
Treatment for cyanosis should always be guided by a doctor. Treatment may vary, as cyanosis can occur for different reasons. The doctor may consider the following interventions:
- Medications: digoxin, hydralazine and isosorbide are medications that may be prescribed for heart failure, because they improve how the heart contracts and help to relax blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood
- Surgery: this procedure is indicated to correct any abnormal strucutres or functions in the heart to improve blood circulation. It may performed for patients with blue baby syndrome or congenital heart disease;
- Ventilation or oxygen therapy: these are indicated to improve oxygenation and breathing in cases of asthma, pneumonia and COPD
Cyanosis caused by prolonged cold exposure can be treated with hot water bottles and warmer clothing. It is important to avoid soaking cold extremities in hot water, as this can cause skin damage.






























