The main symptom of dengue os a higher fever that emerges suddenly and lasts for 2 to 7 days. In addition, you may also notice symptoms like general malaise, nausea, vomiting, headache, excessive fatigue and red rashes.
Dengue symptoms are non-specific, which means they can be confused for symptoms of other illnesses, like a flu, cold, malaria or meningitis. It is important to monitor your symptoms and to see your doctor if you suspect dengue. That way the doctor can confirm a diagnosis and start appropriate treatment.
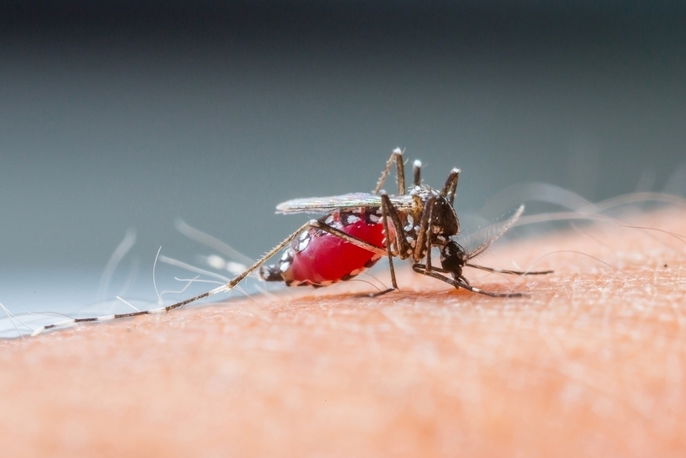
Dengue is an illness caused by a virus that is transmitted to people through an insect bite, specifically from a Aedes aegypti mosquito.
How to know if you have dengue
If you think you may have dengue, report your symptoms below to assess your risk:
If you suspect you have dengue, ensure you drink lots of fluids and book an appointment to see your doctor. In the meantime, you can take acetaminophen to help treat any pain or fevers. Avoid taking aspirin, as it can increase your risk for hemorrhage.
Symptoms of classic dengue
Classic dengue symptoms are very similar to those of Zika. However, they are often more intense and last for 7 to 15 days, while Zika usually resolves within 1 week. In any case, it is important to see your doctor for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring.
Symptoms of dengue usually include:
High fever
A high fever appears very suddenly and temperatures range from 39 to 40ºC (or 102.2 to 104ºF). This fever is a sign that the body is starting to combat the virus through the production of antibodies. Therefore it is important to rest so that your body’s energies are directed to eliminating the virus.
How to treat: You should use medication like acetaminophen as directed by your doctor to regulate your fever.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are other symptoms that are common for dengue, which happen due to general malaise associated with the disease. It can also cause loss of appetite and repulsion to strong odors.
How to treat: You should eat small meals and avoid food that is too hot or cold, as these can worsen malaise. You should opt for meals that are easy to chew and digest, and avoid excess salt, pepper and spices.
Headache and eye pain
The headache usually affects the eye areas and tens to worsen when straining or moving the eyes.
How to treat: Take medication to manage pain, like acetaminophen, and apply warm compresses on your forehead. You may also take soothing teas like ginger tea, sweet grass, lavender or chamomile tea.
Red rashes
The red rash that can appear is very similar to a measles rash, however it mostly affects the chest and arms. This illness can be confirmed through the ribbon test, which involves tying a string on a finger to see whether a rash emerges around it. This test can be used to distinguish dengue from Zika.
How to treat: These rashes disappear once dengue treatment is started, therefore the rash itself does not require a specific treatment. Nonetheless, you should avoid direct trauma to the skin as it can cause bleeding.
General malaise and extreme fatigue
When fighting the virus, the body will use up more energy, which can lead to extreme fatigue. It is also common to eat less during a sickness, which can make the body weaker and more tired.
How to treat: You should rest as much as possible, drink lots of water to eliminate the virus and avoid going to work or school. You should also hold off on any heavy, physical activity around the house.
Abdominal pain, or bone or joint pain
Abdominal pain occurs mostly in children, although bone and joint pain can affect all patients. In addition to pain, the affected region can also appear mildly swollen or reddened.
How to treat: Use medications like acetaminophen to relieve pain, and apply cold compresses to affected areas to help with swelling.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic dengue
Symptoms can appear 3 days after classic dengue, and can include:
- Bleeding from the nose, gums or eyes
- Persistent vomiting
- Blood in the urine
- Agitation and drowsiness
- Confusion
In addition to these symptoms, in some cases, it is also possible to notice symptoms like moist skin that is pallid and cold and decreased blood pressure.
What to do if you suspect hemorrhagic dengue: Proceed immediately to the hospital for assessment, as this condition is life-threatening if left untreated.
How it is treated
Treatment for dengue involves the use of analgesics and fever medications as directed by the doctor. You should not take aspirin, as it can trigger a bleed. To complement treatment, rest and increased fluid intake is also advised. Hemorrhagic dengue treatment should be done in the hospital with IV medication and platelet transfusions as needed.
In serious cases that require hospital admissions, dengue can lead to complications like dehydration, liver problems, blood disease or heart or lung problems.
Dengue symptoms in babies
Dengue may be more difficult to diagnose in babies and children, as it can present similarly to other common infections. Therefore, if the baby presents with a sudden high fever, you should seek an assessment right away so that dengue can be confirmed or ruled out and treatment can be intiated.
Symptoms in babies can include:
- High fever: from 39 to 40ºC (or 102.2 to 104ºF)
- Irritability
- Lack of appetite
- Diarrhea and vomiting
What to do if you suspect dengue infection in a baby: Take the baby to the closest pediatrician or emergency room for assessment and diagnosis.
Generally, treatment is completed at home. Offer the baby plenty of fluids, like water, tea and fresh fruit juices. You should opt for easy-to-digest meals, like boiled vegetables or fruits or boiled chicken or fish. The child may be asymptomatic, which can make diagnosis more difficult.
To prevent dengue, it is important to avoid attracting mosquitos by making sure that potted plants have plenty of soil and that you do not have any accumulation or bodies of water in your yard. You should also use natural mosquito repellents to prevent bites.
Difference between dengue and COVID-19
Dengue and COVID-19 are two very different infections which can cause similar symptoms like general malaise, body aches, fever, fatigue or headache. Learn more about how COVID-19 is transmitted and treated.
There are some symptoms that can help differentiate each type of infection:
The best way to confirm which type of infection you have is to see a doctor for testing and diagnosis. The doctor will likely order bloodwork and send a phlegm sample for testing.






























