Dilated pupils normally occur as a result of stressful situations, fear, pain or after using eye drops for ophthalmologic tests. These conditions do not require any specific treatment.
However dilated pupils that emerge with other symptoms, like confusion, agitation, headache, nausea or intense sweating, may be a sign of a medication overdose, illicit drug use or a brain tumor. These symptoms should be assessed by a doctor immediately so that the underlying cause can be identified.
Dilated pupils that persist or occur with other symptoms should be assessed by a doctor, so that appropriate treatment can be initiated. Treatment may include medications or even surgery, depending on the cause.
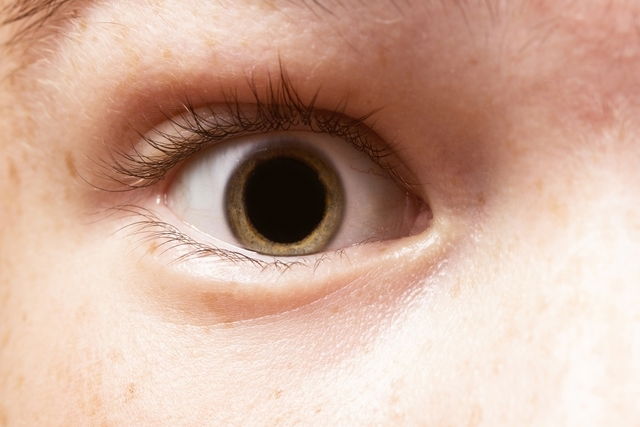
Why are my pupils dilated?
Dilated pupils can be caused by:
1. Mental alertness
Stressful, tense or fearful situations can lead to increased mental alertness, which can dilate both pupils and cause other symptoms like an accelerated heart rate, rapid respiration and pallor.
A physical attraction may also provoke a similar mental status, leading to dilated pupils. However, pupil circumference is not a reliable or measurable indicator of sexual desire or attraction.
When to worry: Dilated pupils caused by increased mental alertness are not a medical problem, as the pupils usually return to their normal size within a few minutes, once the body relaxes.
2. Pain
Pain caused by direct blows, kidney stones or surgery, for example, can lead to dilated pupils, depending on pain intensity. These cases may also cause other symptoms, like fast heart rate and rapid breathing.
When to worry: In this case, pupil dilation tends to resolve once the pain is managed. The doctor may recommend analgesics, like acetaminophen or NSAIDs, to be used as prescribed.
3. Certain eye drops
Eye drops that are used specifically for ophthalmologic tests will purposely dilate the pupils. This allows for better visualization within the eye. Some patients may also report blurry vision and increase light sensitivity upon using these eye drops.
When to worry: Pupils will usually return to their normal size within 3 to 8 hours, however pupils may remain dilated for up to a day in some people.
When pupils are dilated, patients are advised to avoid driving and performing other life-threatening tasks. Patients who report light sensitivity can wear sunglasses until the pupils return to their normal size.
4. Illicit drug use
Some illicit drugs, like amphetamines and cocaine, can cause psychological and behavioural changes, like agitation or anxiety. They may also trigger dilation of the pupils, and other symptoms like chest pain and intense sweating.
When to worry: In this case, the dilated pupils tend to improve as the drug’s effects start to wane, without any specific interventions. However, symptoms like intense agitation, chest pain or shortness of breath may be a sign of a serious drug overdose which require immediate medical attention.
Illicit drug use is not recommended, and patients who suspect they may have a drug dependency should see a doctor for assessment and treatment as necessary.
5. Medication overdose
Anticholinergic medications (like antidepressants, antihistamines and antispasmodics) that are used in higher-than-prescribed doses can lead to an overdose.
In addition to dilated pupils, a medication overdose can cause symptoms like confusion, skin redness, dry mucous membranes and fever.
When to worry: If you suspect a medication overdose, proceed to the closest emergency room for a thorough evaluation and treatment. Treatment may include sedative medications and IV hydration.
6. Head trauma
Blows to the eyes may damage the iris, leading to a dilated pupil. The pupil in the affected eye may have an abnormal shape and may react slowly to a light stimulus.
When to worry: Pupil dilation caused by head trauma usually resolves within a few weeks without any specific treatment. However, some people may experience chronic dilation, depending on the extent of the injury. These patients should be evaluated by an ophthalmologist for treatment, which may involve surgery.
7. Brain tumors
Brain tumors may cause dilated pupils as well as symptoms like headache, nausea, vomiting, seizures, weakness in certain areas of the body and transitory vision loss. Learn more about brain tumor symptoms, and how symptoms can different depending on the area of the brain affected.
When to worry: If you suspect you may have a brain tumor, proceed to the closest emergency room for assessment and testing. The doctor will likely order a brain CT or MRI to confirm a diagnosis.
With brain tumors, dilated pupils tend to improve when the cancer becomes managed.






























