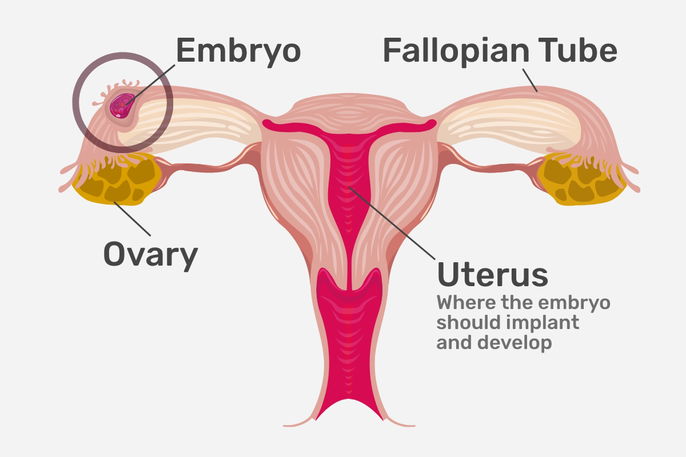
An ectopic pregnancy is a health condition in which an embryo implants and develops outside the of uterus, in areas like the fallopian tubes, ovaries, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
An ectopic pregnancy can occur at week 6 to 8 of pregnancy, and may vary in how it presents. Some women may not notice any symptoms, while others may notice mild symptoms like abnormal vaginal bleeding and mild abdominal pain.
However, in severe cases of ectopic pregnancies, a fallopian tube can rupture and lead to heavy bleeding, intense lower abdominal pain and fainting. In these cases, you should proceed immediately to a hospital for assessment and treatment.
Common symptoms
Some early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are:
- Irregular, watery or dark brown vaginal bleeding
- Mild abdominal or lower back pain
- Mild cramps only on one side in the lower belly
- Lower back pain
- Breast sensitivity
A fallopian tube rupture is a serious condition that can cause bleeding, sudden and intense pain in the lower abdomen, shoulder pain, weakness, dizziness and fainting. In this case, you should seek urgent medical attention for prompt treatment.
However, it is important to note that not all women with an ectopic pregnancy experience symptoms. In these cases, it is only discovered during prenatal consultations or tests.
Confirming a diagnosis
An ectopic pregnancy is typically discovered during regular prenatal consultations with the obstetrician, who will assess any presenting symptoms as well as the woman's health history.
To confirm a diagnosis, the doctor will order tests such like an hCG blood test, transvaginal ultrasound and diagnostic laparoscopy.
The doctor may also opt to order an MRI to rule out other conditions that can present similarly to ectopic pregnancy, such as uterine fibroids, ovarian torsion, appendicitis, miscarriage and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Possible causes
Ectopic pregnancies occur when an embryo fails to move through the fallopian tube due to damage in this organ.
Factors that can increase the risks for an ectopic pregnancy are:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- STIs
- Fallopian tube surgery
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Infertility
- Tumor
Furthermore, women over the age of 35, who smoke, have used an IUD or have had in-vitro fertilization are at an increased risk for an ectopic pregnancy.
Types of ectopic pregnancy
Depending on the location affected, the types of ectopic pregnancy are:
- Tubal pregnancy: this is the most common type of ectopic pregnancy, where the embryo attaches itself to the inside of one of the fallopian tubes
- Cervical pregnancy: occurs when the embryo develops in the cervix
- Caesarean scar pregnancy (CSP): although very rare, the embryo can develop in the scar of a woman's previous cesarean section
- Ovarian ectopic pregnancy: occurs when the embryo attaches to the ovaries
- Heterotopic pregnancy: occurs when the embryo develops between the uterus and the fallopian tube
- Interstitial ectopic pregnancy: occurs when the embryo develops in the part of the tube that passes through the tissue of the uterus
In addition, there is also an abdominal ectopic pregnancy, which happens when the embryo develops in the abdominal cavity or attaches itself to the intestines, urethra or other organ.
Treatment options
Treatment should be directed by an obstetrician and involves medication and surgery.
1. Medicine
Methotrexate, in a single oral dose, is the medication that can be prescribed by the doctor when the embryo does not show cardiac activity, when hCG levels are below 5,000 mIU/mL and if the woman does not present with abdominal pain. The doctor will prescribe this medication if the woman is planning for a pregnancy in the future.
Also recommended: Methotrexate: Uses, How to Take, Dosing & Side Effects tuasaude.com/en/methotrexateMethotrexate can also be administered via intramuscular injection, and is indicated in cases of ectopic pregnancies that occur in an atypical location.
2. Surgery
Surgery is the most recommended treatment for ectopic pregnancy, and can be performed through laparotomy. It is advised for cases of a fallopian tube rupture with hemodynamic instability, in which the body is unable to maintain a normal blood pressure.
In other cases, laparoscopy is more recommended. It involves a smaller incision than a lapartomay, and therefore is associated with a faster recovery time and shorter hospital stay.
A salpingectomy involves partially or completely removing the fallopian tube, and is indicated in cases of irreparable damage to the fallopian tubes.
Possible complications
The main complication of ectopic pregnancy is heavy bleeding from blood vessel rupture, which can be life-threatening.






























