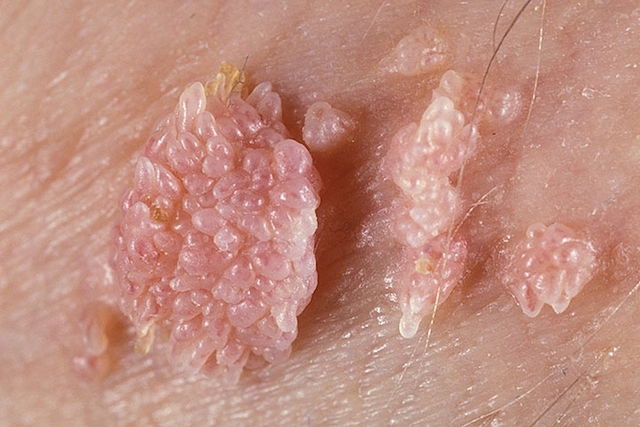
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the HPV virus. They present as pink lesions with a cauliflower-like appearance, which may appear on clusters or on their own.
Genital warts, also known as condyloma acuminatum can affect both men or women, and appear in areas that have come into contact with the virus, such as the vagina, labia majora, penis shaft, scrotum or anal area.
Also recommended: HPV: Symptoms, Types, Transmission & Treatment tuasaude.com/en/hpv-symptoms-transmission-cure-and-treatmentGenital warts can be treated with the use of ointments, acids, cryotherapy, and electrocautery applied directly to the wart. Surgical removal of large or painful warts may also be recommended.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of genital warts are:
- Cauliflower-like lesions on the anus, penis or vagina;
- Small warts that can spread and form large masses;
- Itching, burning or pain in the wart area;
- Skin-colored, pink, brownish or reddish warts;
- Rough texture when palpated
Genital warts can also bleed or have secretions. They are most commonly found on on the penis shaft, scrotum, vagina, labia majora or perianal area. However, these warts can also grow on the lips, cheeks, tongue or throat.
In some cases, genital warts can develop internally, in the vaginal canal or anus, which are associated with a higher risk for cervical or anal cancer.
Also recommended: Warts on Penis: What Causes Them, Symptoms & Treatment tuasaude.com/en/warts-on-penisConfirming a diagnosis
A genital warts diagnosis starts with an evaluation of your symptoms, health history and sexual history. The doctor will then physically examine the warts in the area.
In some cases, the doctor may perform a skin biopsy and collect a sample of the wart to confirm a diagnosis and rule out other conditions that can present similarly, like molluscum contagiosum, condyloma planum, secondary syphilis or a benign nevus, for example.
Men with suspected genital warts may undergo a peniscopy, which allows for the identification of very small warts on the penis that are not visible without a special instrument. For women, the doctor may additionally perform a pap smear to identify the type of HPV present and whether there are any other changes in cervical tissue that could indicate cancer.
Also recommended: Pap Smear: What Is, How it Works & Results tuasaude.com/en/pap-smearPossible causes
Genital warts, or condyloma acuminatum, are caused by HPV, usually type 6 or 11. These types transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse with a person infected with the human papillomavirus.
This virus infects the skin and mucous membranes, causing the appearance of one or more warts in the genital region.
How is it transmitted?
Genital warts are transmitted through skin-to-skin, unprotected contact in the genital or oral region. Penetration is not necessary for transmission to occur.
Although it is less common, HPV can also be transmitted from mother to baby during vaginal delivery.
Treatment options
Genital warts should be treated as directed by a gynecologist or urologist, and usually involves the use of creams and ointments. However, in some cases the doctor may recommend removing the warts with a laser, cryotherapy or surgery.
Complete treatment duration can take up to 2 years and, sometimes, after treatment, lesions on the genitals reappear.
Read more about how to get rid of genital warts and the treatment options available.






























