Hives, or urticaria, are an allergic skin reaction characterized by swollen, red spots that itch. They can be caused by mosquito bites, a fabric allergy or changes in temperature.
Typically, hives symptoms last for up to 24 hours and disappear without leaving any marks or scarring. With chronic urticaria, however, the spots can disappear, then return on other parts of the body and remain for about 6 weeks.
Hives can be controlled by avoiding the irritants that cause them, and with the use of medication (e.g. allergy medication) in some cases.
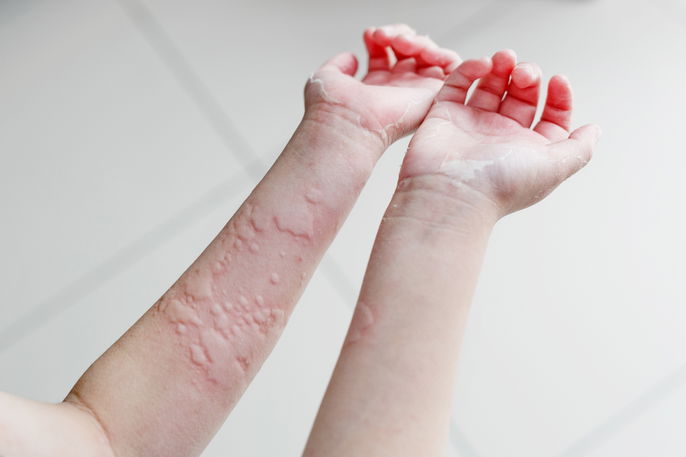
Common symptoms
The main symptoms of urticaria are:
- Red spots of various sizes on the skin
- Pink or reddish plaques on the skin
- Red welts
- Skin swelling
- Intense itching
These symptoms can be localized to a specific region of the skin or cn spread throughout the body. They generally last up to 24 hours, and resolve without leaving marks or scars.
However, the spots can appear again on other parts of the body, remaining for around 6 weeks, this type of hives being called chronic urticaria.
Also recommended: 19 Causes of Red Spots On Skin (with Pictures & Online Quiz) tuasaude.com/en/red-spots-on-skinIn cases of a severe allergic reaction or anaphylaxis, symptoms may appear, such as swelling of the lips, tongue, throat or eyes, difficulty breathing, dizziness or fainting. In these cases, you should seek urgent medical assistance.
Main causes
Causes of hives can vary, but the most common causes include:
- Insect bites
- Allergies to fabric, pollen, latex or sweat
- Color additives in food, or preservatives
- Excess stress
- Heat or extreme cold
- Certain foods, like peanuts, eggs or seafood
- Infections like mononucleosis
- Medication
- Cleaning products, toxic products or poisonous plants
- Certain illnesses, like lupus or leukemia
It is not always possible to determine the cause of hives, but your doctor or allergist can order bloodwork or complete allergy testing to better understand your symptoms and determine a treatment plan.
Types of hives
Hives can be characterized as acute or chronic, depending on the length of the initial allergy. They are often labeled based on their cause:
1. Acute urticaria
Acute urticaria is caused by contact with an allergenic substance that causes the release of histamine in the body. These increased histamine levels can lead to symptoms, which can last up to 24 to 72 hours and may take up to 6 weeks to disappear.
2. Chronic urticaria
Chronic urticaria is characterized by symptoms lasting 6 weeks or more and may reappear over months or years.
3. Stress hives
Emotional or nervous urticaria, also referred to as stress hives, is related to emotional factors, such as excess stress or anxiety. Symptoms tend to become more intense during tense periods.
4. Cholinergic urticaria
Also known as a heat rash, cholinergic urticaria hives emerge with increases in body temperature from hot tubs, from eating spicy or hot food or from physical activity. It usually lasts for about 90 minutes.
5. Gestational urticaria
Gestational urticaria can be caused by stress, food allergies, insect bites or medications. It can also occur due to sensitivity for hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, such as increase prolactin and progesterone.
6. Urticaria pigmentosa
These hives are triggered by excess mast cells from the immune system appearing in the skin. These are most commonly seen in babies and children.
7. Contact urticaria
Contact urticaria tends to arise after direct contact with irritating allergens like latex or resin.
8. Solar urticaria
Solar urticaria, often referred to as a sun allergy, is one of the least common types of urticaria, and is caused by sun exposure. It leads to an exaggerated reaction of the immune system to the sun's rays, causing an inflammatory response in the regions most exposed to the sun, such as arms, hands, neck, chest and face.
Also recommended: Sun Poisoning: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention tuasaude.com/en/sun-poisoning9. Urticarial vasculitis
Urticarial vasculitis is the most rare type of hives. These hives cause inflammation in the veins, leading to pain and burning in affected regions.
Treatment options
Treatment for hives should be guided by a dermatologist, allergist or family doctor, and generally involves the use of medicines to relieve symptoms.
The main remedies that may be prescribed by your doctor for the treatment of urticaria are:
- Antihistamines, such as fexofenadine, loratadine, diphenhydramine or cetirizine;
- Corticosteroid ointments, such as hydrocortisone or dexamethasone;
- Corticosteroids in tablet form, such as prednisone or prednisolone;
- Biological therapy, such as omalizumab;
- Immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine or tacrolimus
These medications should always be prescribed by a doctor, according to the severity of the symptoms and underlying causes.
In serious cases of anaphylaxis, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, with injectable adrenaline, antihistamines or corticosteroids, in addition to maintaining clear airways.






























