Ketones in the urine are caused by increased fat breakdown in the body. When carbohydrates are no longer available for energy, the body resorts to breaking down fat instead. Ketones, therefore, are a by-product of fat metabolism. This condition is also referred to as ketonuria.
Ketones levels in the urine can rise as a result of extended periods of fasting, very strict diets or diabetic ketoacidosis. A ketogenic diet for example, promotes increased fat burning in the body, which can lead to ketones in the urine.
Doctors usually order ketone urine tests for people with type 1 diabetes with the purpose of checking their body's response to treatment. This means that, in people with diabetes, high ketone levels can indicate that the insulin treatment is not being done correctly or that it needs to be readjusted.
Main causes
Ketones in the urine may be caused by several conditions, such as:
- Untreated diabetes
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Extended fasting
- Pancreatic problems
- Excessive exercise
- Diets low in carbohydrates and rich in fat, like a keto diet
- Pregnancy
- Fevers, especially from infections
- Frequent vomiting
Having high levels of ketones in urine is not always a sign of a health condition, since it can be caused by simple lifestyle changes, such as restrictive diets or exercise.
Nonetheless, having high ketone levels, especially if accompanied by symptoms such as nausea, fatigue or confusion, may indicate some type of health problem that needs proper treatment in order to avoid serious complications. Therefore, it is always recommended for the test results to be evaluated by a physician.
Common symptoms
When there are high ketone levels in the urine, it is also common to find blood in the urine sample. Other than that, high ketone levels can also be identified through some symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent need to urinate, fatigue, metallic taste inn the mouth, or nausea.
The main symptoms that can indicate ketones in the urine include:
- Excessive thirst
- Increased urinary frequency
- Foul breath with metallic taste
- Fatigue
- Red skin
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
Normally, when ketones are found in the urine, they will also be present in the blood. This is known as a state of ketosis.
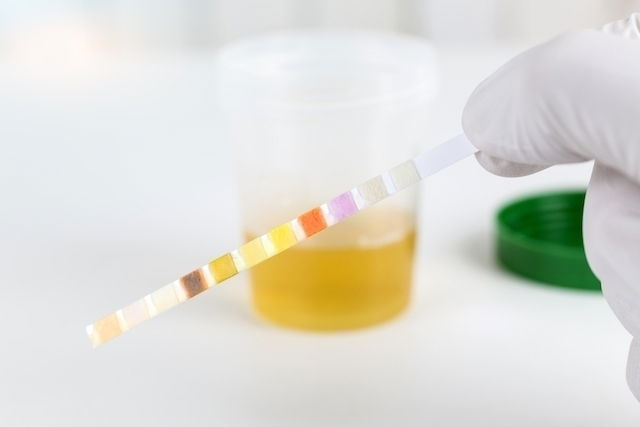
Ketone test
The presence and approximate amount of ketone bodies in the urine can be measured using a conventional urine strip test, where you can see the color change on the test strip. However, it is not possible to know the exact concentration of ketone bodies urine this strip test. Therefore, an assessment by a doctor is necessary to investigate the cause of the presence of ketone bodies.
A second urine test may be ordered to confirm the presence of ketone bodies in the urine, as the patient's hydration level can interfere with the result, giving false-positive results when the person is dehydrated, or false-negative results when the person drinks a lot of water.
In addition, to find out the amount of circulating ketone bodies, a blood test may also be ordered. If the concentration of ketone bodies in the blood is higher than 0.5 mmol/L, this could be a sign of illness.
How to treat
High levels of ketones in urine should always be investigated by a doctor, and treated as needed. This is because an accumulation of ketones in the blood can result in several health problems such as dehydration, electrolytic unbalance, acidosis, and even coma.
From the moment ketonuria is identified, doctors may prescribe the use of insulin, fluid replacement through IV, or some dietary changes in order to achieve ideal amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fat in the diet.






























