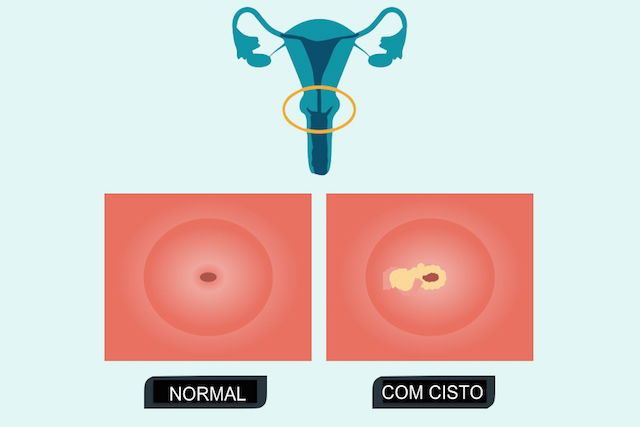
A Nabothian cyst is a small cyst that can form on the surface of the cervix. It typically forms due to increased discharge production in the Nabothian glands. If the gland becomes inflamed, infected or produces more discharge, discharge is unable to be eliminated normally, leading to obstruction of the gland and the formation of a cyst.
Nabothian cysts are quite common in women of reproductive age and are considered to be benign. Specific treatments to get rid of them are not usually necessary.
However, when several cysts are present or when the cyst continues to increases in size over time, it is important to consult a gynecologist to assess the need for a removal.
Main symptoms
The formation of Nabothian cysts does not usually cause symptoms. It is typically only identified during a routine gynecological examinations, in which the gynecologist will note a small, round, white or yellow cyst that does not hurt or cause discomfort.
In some cases, the presence of more than one cyst may be seen, and multiple cysts may also not cause symptoms. However, they can also cause bleeding outside the menstrual period, pelvic pain or discharge, all which should be assessed and tested to rule out other possible causes, like an infection.
What causes a Nabothian cyst?
Nabothian cysts occur due to a build-up of discharge inside the uterus due to the blockage of mucus in the Nabothian gland. This obstruction can occur due to an infection and inflammation in the genital region, in which the body forms a layer of protective skin in the region of the cervix. This can lead to several small benign nodules in the area, which can be palpated or visualized during vaginal exams.
In some women, the cyst may also appear as a result of cervical trauma or after vaginal birth, as these conditions can promote tissue growth around the gland, leading to the formation of a cyst.
Confirming a diagnosis
A Nabothian cyst is usually identified during a routine gynecological exam, although the doctor can order additional tests to evaluate the pelvic region, such as a pelvic ultrasound, MRI or CT scan. The doctor can also order a colposcopy to further visualize the vaginal tract.
If abnormalities are observed in the vaginal exam and tests, the doctor may request a biopsy of the cyst to rule out malignancy and the need for a more targeted treatment.
Do Nabothian cysts affect fertility?
A Nabothian cyst does not cause any changes in fertility, as it is related to the obstruction of the Nabothian glands that produce mucus, present on the surface of the uterus. Therefore, women who have fertility issue should see a gynecologist for assessment, as it may be related to other causes.
Treatment options
Nabothian cysts do not require treatment as they are typically benign and do not cause symptoms. They often do not pose a health risk and typically resolve on their own. However, if the Nabothian cyst is related to a genital infection, the doctor may recommend the use of medications to combat the infectious agent, preventing complications.
In some cases, the presence of several cysts or an increase in the size of the cyst over time may be observed during a gynecological examination, altering the shape of the uterus. Therefore, in these situations it may be necessary to remove the cyst through electrocautery or with a scalpel.






























