Phimosis surgery, also called circumcision or postectomy, aims to remove excess skin from the penis. It is performed to prevent penile cancer, urinary tract infections and sexually transmitted infections.
Phimosis surgery is carried out by a urologist or pediatric surgeon under general or local anesthesia and is a safe and simple procedure. It is commonly indicated for boys between 7 and 10 years of age, but it can also be performed in adolescence, although recovery may be more painful.
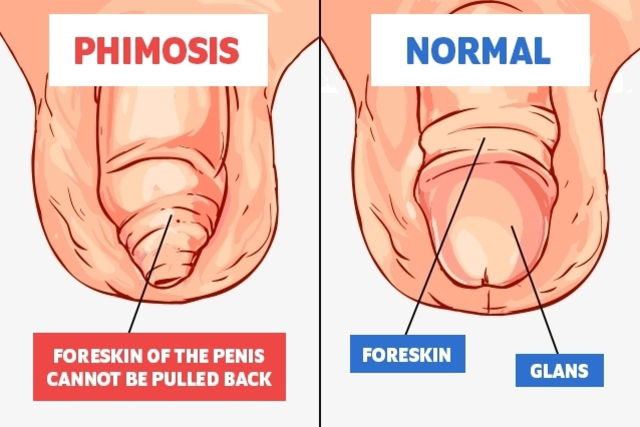
Phimosis is characterized by excess skin on the head of the penis, which causes difficulty in exposing the glans. Although this excess skin and difficulty exposing the glans can resolve within the first year of life, it can also appear in adulthood as a result of skin changes or infection.
How it's done
Phimosis surgery is performed by a urologist or pediatric surgeon, under sedation, local or general anesthesia. depending on the patient's age. The surgery is considered to be simple and quick and consists of removing excess skin at the site, so that the glans can be exposed.
During the procedure, in addition to sedation or anesthesia, a penile nerve blocker is also administered, as this ensures that the patient does not feel any discomfort during the procedure.
Benefits of surgery
The goal of phimosis surgery is to remove the foreskin, or excess skin that covers the penis. This facilitates exposure of the glans, which has the following health benefits for men:
- Decreased risk of penile infection (e.g. like a yeast infection)
- Decreased risk of urinary tract infection
- Prevention of penile cancer
Phimosis surgery is also associated with a reduced risk for sexually transmitted infections, such as HPV and HIV, for example. However, it is important to remember that this surgery does not eliminate the need to use a condom during any intimate contact, as condom use is the only way to be completely safe from STIs.
Recovery and wound care
Recovery after surgery is relatively quick and in about 10 days there is no pain or bleeding. By the 8th day, patients may feel some slight discomfort and bleeding as a result from nocturnal erections. This is why it is recommended you do this surgery in childhood - decreased incidence of nocturnal erections is more conducive to healing.
After surgery, the doctor may advise you to change the dressing the following morning. This is done by gently removing the gauze and then rinsing the area with soap and water, being careful not to aggravate the wound and make it bleed. Then apply the anesthetic ointment prescribed by your doctor and cover the wound again with a sterile gauze, so that it is always dry. The stitches are usually removed on the 8th day.
To promote a quicker recovery from a circumcision, it is recommended you:
- Avoid any exertion or physical activity for the first 3 days, and rest;
- Apply an ice pack on the area to decrease swelling or whenever pain is felt;
- Take analgesics as prescribed by your doctor;
- Do not have sex for at least 1 month after surgery.
After this period of rest and care, it is possible to visualize the the final results of the surgery.
Possible risks
This surgery is typically performed in a hospital setting and has few health risks. It is usually well-tolerated and recovery is rapid. Although they are rare, complications can occur. These include bleeding, infection, narrowing of the urethral meatus, excessive or insufficient foreskin removal and preputial asymmetry, with possible need for further surgery.