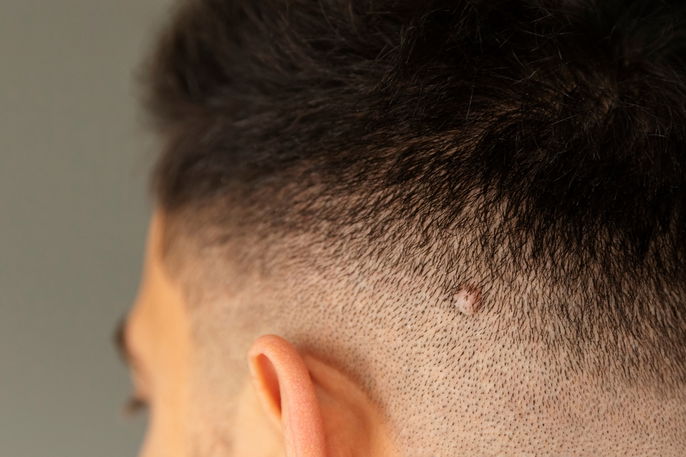
A sebaceous cyst is a small, round lump that forms under the skin and is smooth to the touch. Sebaceous cysts can occur anywhere on the body, however they are more commonly found on the scalp, ears, neck, back, and face.
Sebaceous cysts are benign (not cancerous) and are caused by a blockage of the sebaceous glands. An accumulation of sebum, an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands, causes a lump to form. Sebaceous cysts typically do not cause any symptoms, however a cyst that becomes inflamed may be tender, painful, red, and warm to the touch.
The term sebaceous cyst is often used to refer to an epidermoid or pilar cyst, however these cysts differ because they are keratin filled and do not actually involve the sebaceous glands. Sebaceous cysts are not typically cause for concern and do not usually require treatment. In some cases, however, a dermatologist (skin doctor) will drain or remove the cyst surgically.
Common symptoms
The main symptom of a sebaceous cyst is the formation of a lump under the skin. There may be only one cyst or multiple, which may present with characteristics like:
- A round lump, which can grow bigger over time;
- A soft or firm lump under the skin that is movable with palpation;
- A skin-colored cyst that may appear yellow or greenish due to the fluid that has accumulated;
- A small opening in the center of the cyst, from which an oily substance may drain;
- Discomfort or pain, which depends on the location and size of the cyst.
An inflamed cyst can be painful, and cause warmth, redness, and tenderness of the area. A collection of pus may also form.
A sebaceous cyst can appear on any part of the body, however they are most frequently found on the face, scalp, ears, neck, trunk, and upper back.
Also recommended: Lump Behind Ear: 7 Causes (& When to See a Doctor) tuasaude.com/en/lump-behind-the-earConfirming a diagnosis
A dermatologist or other healthcare provider will make the diagnosis of a sebaceous cyst based on patient history and a physical exam, taking into account the color, size, and consistency of the cyst.
If the cyst appears atypical or abnormal, your provider may recommend tests to rule out malignancy (cancer). These tests may include an ultrasound, computed tomography (CT scan), or a skin biopsy.
Possible causes
A sebaceous cyst is caused by a blockage of the sebaceous glands. Risks for development of a sebaceous cyst include:
- Acne;
- Blackheads;
- Damage to the skin, such as cuts or abrasions.
These conditions can lead to a blockage of the sebaceous glands, which causes a buildup of sebum. This buildup causes a lump to form, which may increase over time as more secretions accumulate.
Treatment options
Sebaceous cysts do not necessarily require treatment, especially if they are small. Applying a warm compress to the area for 15 minutes can help promote dilation (opening) of the sebaceous glands and can help the cyst spontaneously drain. Squeezing (popping) the cyst is not recommended, and can increase the risk for infection and tissue damage, making treatment more complicated.
If a cyst becomes infected or inflamed, a dermatologist may drain the cyst and prescribe antibiotics. Cysts that are very large or aesthetically displeasing can be surgically removed.
Surgical removal
Surgical removal of a sebaceous cyst is relatively simple, and is done by a doctor using a local anesthetic. Surgery is usually indicated for cysts that are larger than 1 cm in diameter or become infected. After the contents of the cyst are removed, a doctor may place a few stitches followed by a bandage. You should receive instructions about follow up care.
Sebaceous cysts are usually benign, however your doctor may send a sample of the contents to the lab to rule out the possibility of cancer. This is especially true for those with a personal or family history of cancer.






























