Skin peeling can be caused by dry skin, a sun burn, contact dermatitis, psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. It is often associated with other symptoms like skin redness, pain, itching or swelling.
Skin peeling can be prevented in most cases through measures like moisturizing the skin, applying sunscreen or using the right hygienic products for your skin type.
Nonetheless, if your skin peels for more than a week, or if the skin peeling is very uncomfortable and causing pain, you should see a dermatologist for further assessment and treatment as necessary.
Why is my skin peeling?
The most common causes of skin peeling are:
1. Dry skin
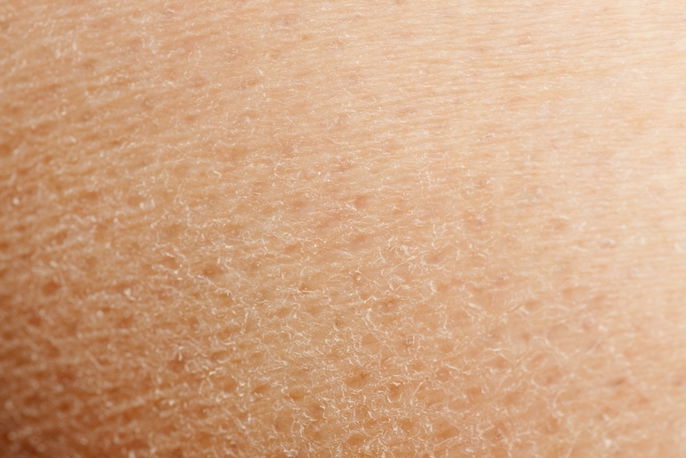
Dry skin, medically known as xerodermia, occurs when the sebaceous glads and sweat glands produce less sweat and oil then usual. This leads to dry skin that ends up peeling.
What to do: You should increase your daily water intake and avoid bathing in very hot water. Try using a mild or glycerin-based soap and moisturize your skin when a cream that is appropriate for your skin type.
2. Sun burn
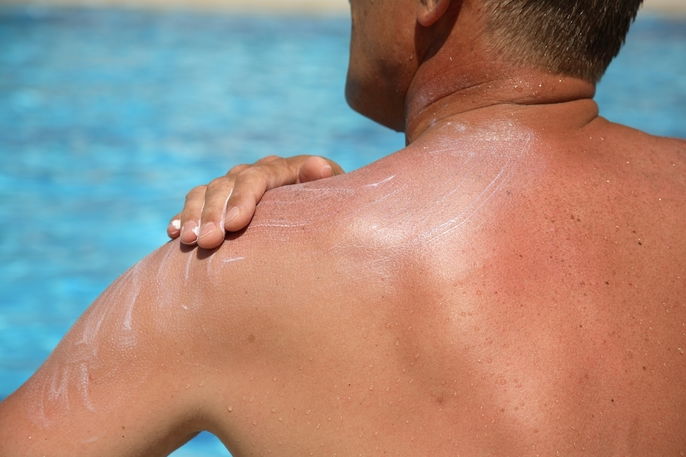
A sun burn occurs following prolonged exposure to the sun without any protection. This leads to UV rays being absorbed by the skin, which can leave the skin red and cause peeling.
Generally, a sun burn is more common in areas that are more prone to be exposed ot the sun, like the face, arms or back.
What to do: You should bathe in cold water and apply after-sun creams to help relieve any discomfort and promote skin healing.
3. Contact dermatitis
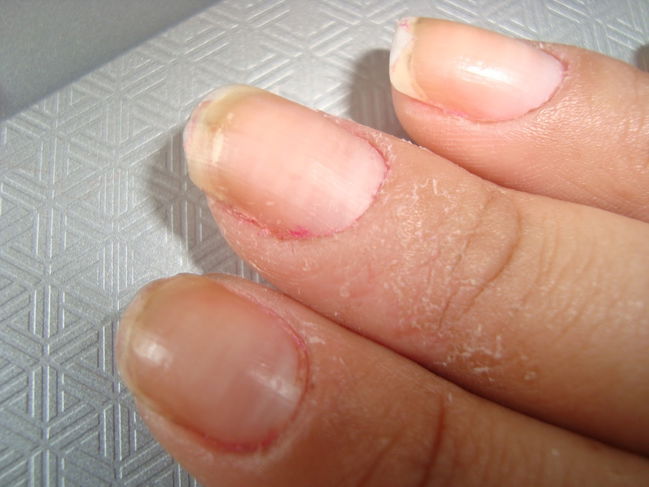

Contact dermatitis occurs when an allergen, like perfume, cosmetics or cleaning products, enters in direct contact with the skin and causes symptoms like redness, itching, wounds and blisters. These symptoms can emerge immediately or up to 12 hours after initial contact, depending on the substance.
What to do: You are advised to avoid contact with the triggering substance, and to was the skin with cold water and pH neutral soap. You can also take an anti-histamine as directed by your doctor to soothe irritation and prevent worsening. If you frequently experience these symptoms, you can perform allergy testing to identify the trigger and start treatment.
4. Psoriasis
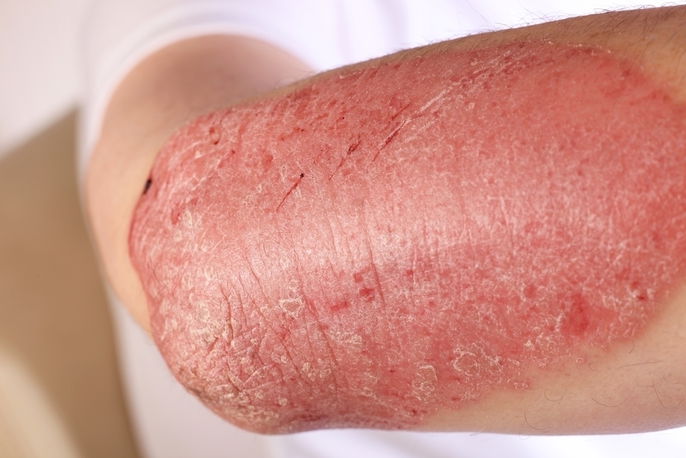
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes by pink or red rashes on the skin that are covered with white, peeling skin. The size of these lesions are variable and can appear anywhere on the body, although the most affected body parts are usually the elbows, knees and scalp. One of the characteristics of psoriasis is skin peeling that may also itch.
Symptom intensity can depend on climate and other factors like stress and alcohol intake. Learn more about the different types of psoriasis and the symptoms it can cause.
What to do: Treatment for psoriasis should be indicated by a dermatologist and is normally done with topical creams or gels. The doctor may also prescribe oral medication or treatment of UV rays. Diet can also play an important role in the treatment of psoriasis. Check-out a recommended psoriasis diet plan curated by our registered dietitian.
5. Atopic dermatitis
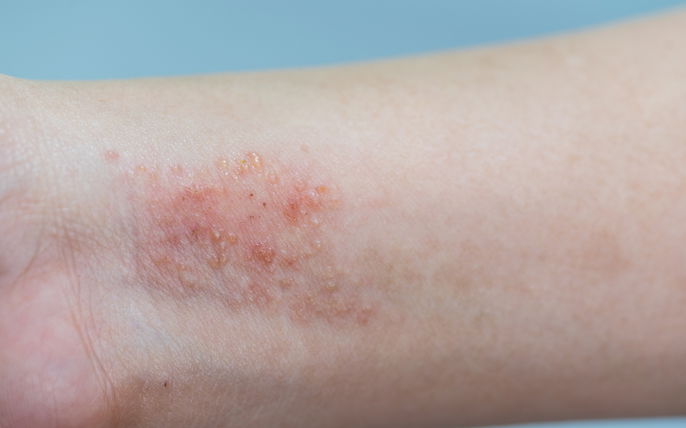
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory disease that causes dry skin. It occurs due to the skin’s inability to retain water and also due to insufficient production of fat by the sebaceous glands, which can increase the skin’s risk for peeling. Atopic dermatitis is associated with intense itching and most commonly affects the elbows, knees, wrists, back of the hands, feet and genital area.
This illness can appear in childhood and tends to improve up until adolescence, although many people experience further episodes in adulthood.
What to do: It is important to ensure your skin is properly moisturized and to drink plenty of water every day, to promote skin hydration. In some cases, you may need to see a dermatologist for treatment, which could include emolient creams and other topical medications.
6. Seborrheic dermatitis
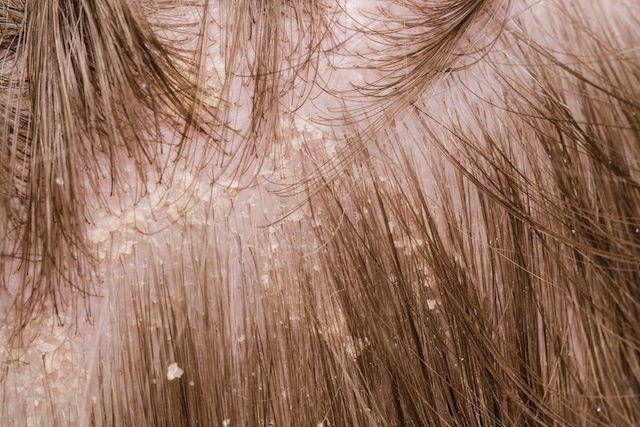
Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease characterized by skin peeling in areas that contain a higher concentration of sebaceous glands, like on the scalp and upper chest or back. When the scalp is affected, seborrheic dermatitis is also referred to as "dandruff", however it can also occur in other areas with hair (like the beard or eyebrows) or areas of the body that bend (like the armpit, groin or ears).
Skin peeling caused by seborrheic dermatitis is normally oily in nature and tends to worsen during periods of stress or with climate changes. It is often accompanied by symptoms like redness and itching.
What to do: While there is no cure for seborrheic dermatitis, there are ways to reduce peeling and itching. Some tips include applying a moisturizing cream, using shampoo that is appropriate fro your skin type, ensuring adequate hygiene and using light clothing.
In more serious cases, you should be assessed by a dermatologist, who may recommend treatment with steroids, like hydrocortisone or dexamethasone. Read more about the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and the options that your doctor may consider.
7. Fungal infection
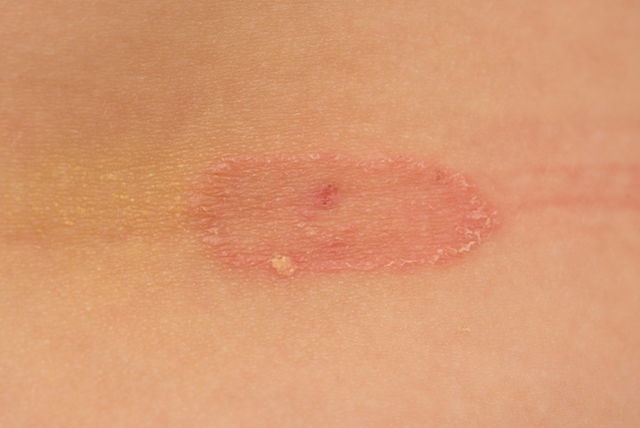
A fungal infection can be caused by many types of fungus and is transmissible between people through direct contact with contaminated objects (especially in hot and humid environments).
Usually, fungal infections cause skin peeling that can be accompanied by skin cracking and itching. The most commonly affected areas are usually hot and humid, like the toes, armpits, groins or between other skin rolls. It is also common for symptoms to worsen with sweating.
What to do: Treatment usually includes the use of topical antifungals that are prescribed by a doctor. To prevent worsening, you should also reduce body moisture when possible by drying the body off following a shower, for example, any by using light clothing. You should also avoid sharing personal hygiene objects.
8. Cutaneous lupus erythmetous
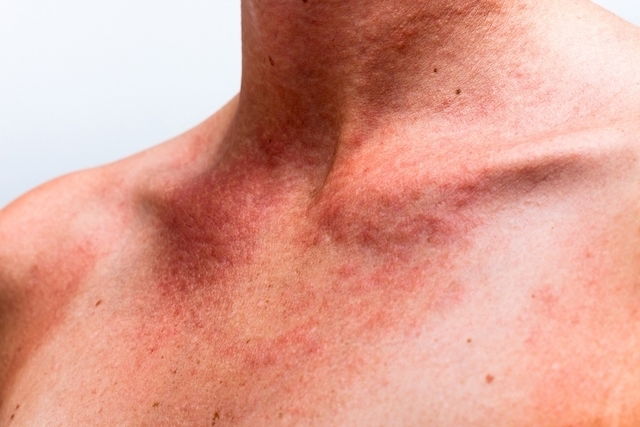
Cutaneous lupus erythmetous is characterized by red skin lesions with a darker, maroon border and by skin peeling. These lesions are usually found in areas of the body that are most exposed to the sun, like the face, ears and scalp.
What to do: Treatment of this illness includes protecting your skin from the sun when possible by using a hat, wearing long sleeve shirts and applying sunscreen. In serious cases, you should see a dermatologist for specific treatment, like using topical corticosteroids and other medications.
9. Skin cancer
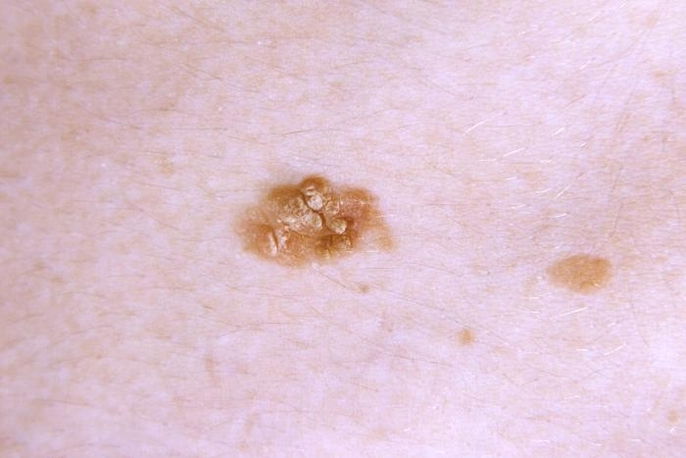
Although this is more rare, skin peeling may be a sign of skin cancer, especially following prolonged sun exposure without any protection.
In addition to peeling, skin cancer can also cause rashes or lesions that are usually asymmetric, contain an irregular border, have more than one color and are over 1 cm in size.
What to do: Treatment for this disease depends on the stage of cancer identified. It may include surgical removal of the lesion, chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The earlier the cancer is caught, the greater the chances of a cure.






























