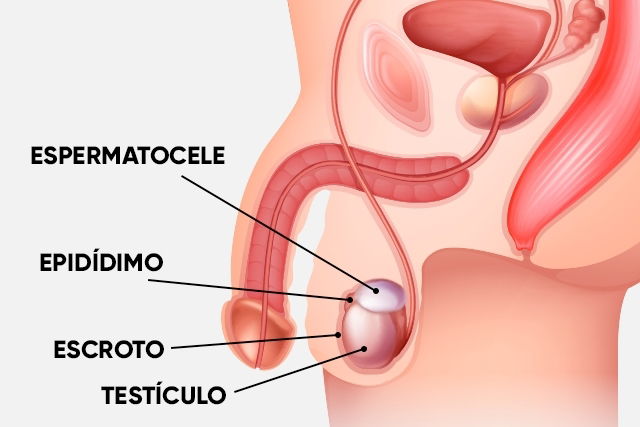
A spermatocele is a small, painless cyst that appears in the epididymis. The epididymis is the structure that connects the vas deferens, which transports sperm, to the testicles. A spermatocele can cause to pain, discomfort or heaviness in the affected testicle, especially if the cyst is large.
A spermatocele, also known as a seminal cyst or epididymal cyst, if often found upon routine palpation during hygiene or during a a health assessment. It is described as a soft, movable lump that can cause some discomfort depending on its size.
Also recommended: Lump on Testicle: 7 Common Causes & How to Treat tuasaude.com/en/lump-on-testicleAlthough this finding is usually benign and not harmful to health, it should still be evaluate by a doctor, as testicular lumps can also be a sign of another health condition, like cancer in rare cases. Normally, a spermatocele does not impact fertility and, therefore, may not always require treatment.
Common symptoms
The main symptoms of a spermatocele are:
- A cyst next to the testicle
- A movable cyst that does not hurt
- Pain or discomfort in the affected testicle
- A feeling of heaviness in genital area
If any abnormalities are noted in the testicles, it is very important to consult a doctor to rule out other more serious causes, such as testicular torsion or even cancer.
Also recommended: Penile Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment tuasaude.com/en/penile-cancerConfirming a diagnosis
A spermatocele diagnosis is confirmed by a family doctor or urologist upon physical examination of the testicles. The doctor will palpate the testicles for the presence of the cyst, and also assess other symptoms that patient may present with.
The doctor may also perform a transilumination test, which consists of shining a light in the scrotal area to better evaluate it. An ultrasound can also help to identify the cyst and determine its characteristics, as well as rule out other possible conditions.
Possible causes
What causes a spermatocele is not fully known, but it is believed to occur due to an obstruction in the tubules in the epididymi, which are responsible for transporting sperm.
It is most likely to occur when the patient has a history of epididymitis, a vasectomy or a strong blow to the area.
Treatment options
Spermatocele treatment should be guided by a urologist, who may recommend:
1. Regular medical follow-up
Since most spermatoceles do not cause any type of complication or discomfort, treatment may not always be necessary.
However, the doctor may advise periodic follow-up, about twice a year, to monitor the cyst and evaluate any changes that may indicate malignancy.
2. Use of anti-inflammatories
If a spermatocele causes discomfort or pain that interrupts your daily routine, the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatories to help reduce swelling in the area.
If symptoms resolve after about one to two weeks of treatment for 1 or 2 weeks, further treatment is usually not necessary.
However, if symptoms persist, a reassessment may be necessary to determine the need for surgical removal.
3. Spermatocele surgery
Spermatocele surgery, also known as spermatocelectomy, is a procedure performed under general anesthesia. It is aimed at separate the spermatocele from the epididymis and removing it.
After surgery, it is usually necessary to use underwear that provided scrotal support to help maintain pressure on the site. This can help to prevent the incision from opening when moving.
What is the recovery from surgery like?
During recovery from spermatocele surgery, the doctor may advise precautions such as:
- Applying cold compresses to the scrotum
- Taking medications as prescribed by the doctor;
- Avoiding getting the surgical area wet until the stitches are removed;
- Having the incision assessed and treated at the clinic or hospital
Although it is rare, some complications may occur following surgery, especially infertility if there is any post-op trauma to the epididymis and/or vas deferens. Therefore, it is very important to select a certified urology clinic with a surgeon with a lot of experience.






























