Warts are small, generally harmless, benign growths on the skin caused by the HPV virus. These growths present as smooth, rough, flat or raised lesions, that can be pink, gray, yellow, brown or black in color.
Warts can appear in groups or on their own, and easily spread from one area of the body to another. They can appear at any age and affect any part of the body, such as the face, foot, groin, genital area or hands.
Normally, warts go away without any specific treatment, however, the dermatologist may recommend prescribe medications to help speed-up their healing, especially when warts appear in the genital area.
Main symptoms
Warts are lesions on the skin, which can present with characteristics or symptoms such as:
- Smooth or rough surface
- Size ranging from 1 to 10 millimeters
- Flat or raised appearance
- Develop on their own or clusters
- Can be the same color as the skin, or present with colors like color, pink, gray, yellow, brown or black
- Itching in the area, in some cases
Furthermore, warts can be dome-shaped or have a cauliflower-like appearance.
The most common places for warts to appear are the hands, feet, face, neck, knees or elbows, but they can also appear in the genital or perianal region.
Despite being benign tumors, it is important to consult a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and type of wart. This will help to guide the most appropriate treatment if necessary.
Confirming a diagnosis
Warts are diagnosed by a dermatologist through physical examination and by observing the characteristics of the skin lesions.
Additional tests are generally not necessary, however, if the doctor suspects other conditions with similar symptoms, such as seborrheic keratosis, lichen planus or skin cancer, he or she may order a skin biopsy.
Types of warts
Warts can be classified into some types according to their location and characteristics:
1. Plantar wart
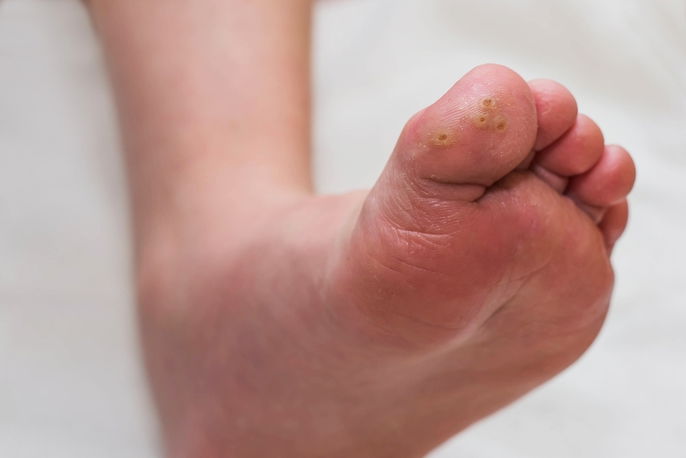
Plantar warts typically found on the feet. They feel similarly to a callus, and are typically yellow in color with littel black dots inside. Read more about plantar warts and the symptoms they can cause.
2. Filiform wart
A filiform wart is a type of wart with a thin and elongated appearance. These appear mainly on the face and neck, and are more common in older adults.
3. Common wart
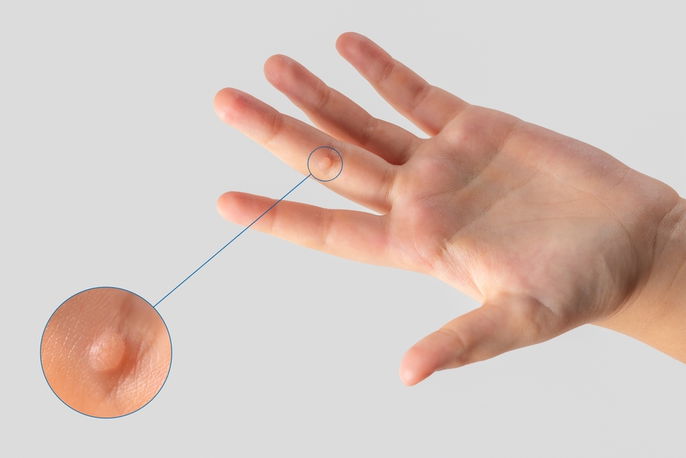
Common warts are generally less than 1 cm in diameter. They are firm and usually have a rough and rounded surface, and their color can vary from skin color to gray, yellow, brown or black.
This type of wart is more common in children and adolescents and most frequently develop on the elbows, knees or hands.
4. Flat wart
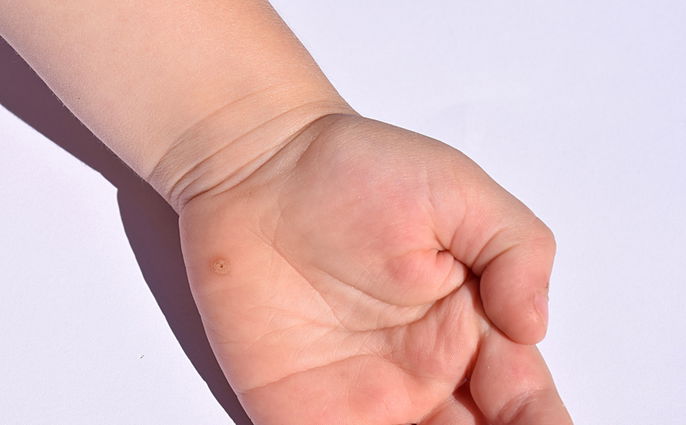
A flat wart is a type of wart that has a flat surface. It is soft and measures at around 1 to 7 millimeters. These typically appear in groups.
This type of wart is most common on the face, and mainly affects eenagers.
5. Genital warts
Genital warts appear on the vagina, labia majora, shaft of the penis, scrotum or anal region. The generally have a cauliflower appearance, and may be single or appear in clusters.
This type of wart is typically transmitted sexually through skin-to-skin contact.
Genital warts can also appear in the internal region of the vaginal canal or anus, and are associated with an increased risk for cervical or anal cancer.
Possible causes
Warts are caused by an infection with the HPV virus which infects the epithelial layers of the skin or mucous membranes. They virus multiplies in this layer and activates the growth of skin cells, causing the lesions.
This virus enters the skin through small cuts, scrapes, or soft spots. It can take 2 to 6 months for the wart to develop after the initial infection.
However, not all HPV infections cause warts, as a person's immune system can fight the virus and eliminate it.
Is HPV the only cause of warts?
HPV is the only cause of warts, however, it is important to note that there are over 100 different types of HPV that cause different types of warts on various parts of the body.
Read more about the HPV virus and the symptoms it can cause.
How warts are transmitted
The transmission of warts occurs through direct contact with these lesions, which allows the HPV virus to pass from one person to another.
Generally, children are most affected, as they tend to pick at their warts.
However, it is important to clarify that viruses only cause the appearance of warts when skin integrity is compromised due to a scratch, dry skin, an ingrown toenail or wound, for example.
Is it normal for a wart to turn black?
Black warts are not a specific type of wart, and although they are usually skin-colored, brown or gray, they can sometimes appear darker.
Generally speaking, these warts are harmless, but they can be uncomfortable or embarrassing.
Some warts may have small black dots. This happens because as the wart grows, it can affect the small blood vessels in the skin, which can clot and appear as small black dots inside the wart.
Treatments options
There are different types of treatment available for the removal of warts that can be recommended by the dermatologist. The type of treatment used depends on the type of wart and its characteristics. There are some home remedies that can be used to help with wart removal, however these are usually used to complement treatment indicated by the doctor.
Some ways of removing warts are:
1. Use of medication
The dermatologist can indicate the use of some creams or ointments made with acetylsalicylic acid or lactic acid. These are applied directly on the wart, and can be used at home at least twice a day (or as prescribed by the doctor).
For genital warts, the doctor may prescribe ointments, such as imiquimod or podophyllotoxin, or the application of acids to the skin.
2. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is the most used and recommended therapy. It consists of the application of liquid nitrogen in spray-form directly on the wart. The wart will usually fall off within a few days.
This treatment should be completed in a doctor’s office to avoid skin burns, as liquid nitrogen is extremely cold.
3. Laser removal
Laser removal is indicated when the patient has many warts or if they are spreading. It is done under local anesthesia, as the procedure without analgesic can cause pain and discomfort. A laser ray is applied directly on the wart to destroy the tissue within the wart.
Following this procedure, patients should take care of the wound that appears after the wart falls off, as there is a risk for infection. This is also important for warts that are physically excised (cut off) by the doctor.
4. Duct tape
Duct tape is an easy way to remove warts, and it is recommended by the American Dermatologic Association. To remove the wart with duct tape, you should cover the wart with duct tape for up to 6 days, then remove the tape and soak the wart for a few minutes. Then file the skin with an emery board or pumice stone to remove the excess skin.
Some of these treatments should be done in the doctor’s office by a dermatologist. Treatments that are applied at home should only be used after approval by your doctor, to ensure you will be treating a wart and not another skin condition.
Check-out other home remedies for warts that you can try to complement the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
How to prevent
To prevent the risk of contamination with warts, you must:
- Avoid touching other people's warts without having your skin properly protected with gloves
- Avoid community swimming pools that are not properly cleaned with specific products
- Do not share other people's towels, clothing or underwear
- Do not share personal objects, such as razors or tweezer or nail clippers
- Avoid biting nails and picking cuticles
Furthermore, it is also advised to avoid walking barefoot in swimming pool changing rooms or other public places, and instead use flip-flops whenever possible.
Another way to avoid getting warts is to get the HPV vaccine, which prevents genital warts, precancerous lesions and cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina or anus. Know where and when to get the HPV vaccine.






























