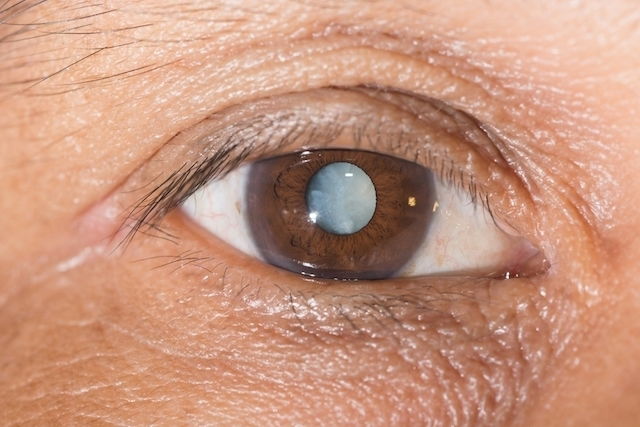
A white spot on the eye is most commonly seen on the pupil, and is associated with health conditions like retinoblastomas, cataracts, cornea ulcers, pterygium or toxocariasis.
In addition to the white spot, you may also notice symptoms like difficulty seeing, blurry vision itchiness and redness.
It is important to see an ophthalmologist for assessment and treatment as necessary if you notice a white spot on your eye.
Common causes
The most common causes of a white spot on the eye are:
1. Retinoblastoma
A retinoblastoma is a rare type of cancer that affect one or both eyes. It is most commonly diagnosed in children.
This condition can be easily identified in babies following birth or during the first postpartum consult with the pediatrician. It is associated with symptoms like difficulty seeing, redness and crossed eyes, in addition to the white spot on the eyes.
What to do: It is essential to consult an ophthalmologist for early diagnosis and treatment as necessary to prevent complications. .
Treatment for a retinoblastoma varies depending on the severity of the disease. Some cases can be resolved with lasers or with a cold therapy to destroy the tumor. Other, more serious cases may require chemotherapy.
2. Cataracts
Cataracts is a disease that is characterized by progressive vision loss. It is most common in people over 60 years of age, which is related to crystallization of the eye. It can start to develop soon after birth (which is referred to as congenital cataracts), and in this case, it occurs due to malformation in the fetus. Congenital cataracts can affect one or both eyes.
The characteristic signs of cataracts are a white sheen on the pupil that can interfere with vision, leading to blurriness or total loss.
What to do: Treatment for cataracts should be started as soon as a diagnosis is confirmed to prevent complications like total vision loss. Normally, treatment is done with surgery, with replacement of the crystalline lens.
3. Toxocariasis
Toxocariasis is an infectious disease caused by Toxocara sp. parasites. These parasites can reach the eye and cause redness and white spots on the pupil, as well as pain, eye itchiness and decreased vision. Ocular txocariasis is more common in children who play on the floor, in the sand or with dirt, as these are common places for the Toxocara
What to do: Cases of toxocariasis can be treated with corticosteroid eyedrops to treat symptoms, as prescribed by an ophthalmologist, to prevent disease progression.
4. Pterygium
Pterygium is associated with a white or yellow flesh growing in the cornea. It causes symptoms like blurry vision, discomfort when blinking, the sensation of sand in the eyes and difficulty seeing.
What to do: You should see an ophthalmologist to prescribe the most appropriate treatment, which may involve analgesic eye drops or lubricant. Serious cases that compromise vision may require surgery.
5. Corneal ulcer
A corneal ulcer is caused by a wound that appears in the eye and causes the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. It also causes symptoms like blurry vision and a white spot in the eye. Ulcers can appear due to eye infections, small wounds, a dry eye or contact with an irritating substance.
What to do: Treatment for a corneal ulcer can vary depending on the underlying cause. The doctor may prescribe antibacterial ointments or eye drops, corticosteroids or even surgery in serious cases.
When to worry
It is important to see an ophthalmologist if you notice any of the following:
- Ocular discomfort
- Difficulty seeing
- Blurry vision
- Nighttime blindness
- Spots in the eyes
- Pain or itchiness
The doctor will be able to confirm a diagnosis through assessment of the eye as well as any additional testing. Once confirmed, treatment can be started.





























