Yellow eyes can be caused by liver, gallbladder or pancreatic diseases, like cirrhosis, gallstones or pancreatitis. These conditions are associated with an excessive accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, leading to yellow eyes.
Yellow eyes are also commonly seen in newborns, and this condition is often referred to as neonatal jaundice. In these cases, the yellows are a sign that the liver is not yet fully developed, which is normal for this stage and is not a sign of a serious problem.
In any case, it is important to consult your family doctor, gastroenterologist or hepatologist if you notice you have yellow eyes. The doctor will order tests to identify the underlying cause and start the most appropriate treatment.
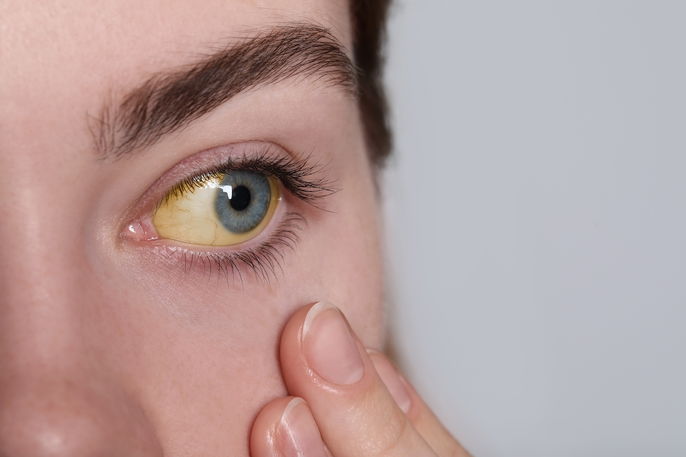
What does having yellow eyes mean?
1. Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver that is generally caused by the hepatitis A, B or C virus. It can also occur due to the use of medications.
This inflammation alters liver functioning, and impairs how bilirubin is transported to the bile ducts. It is absorbed into the bloodstream, leading to the appearance of yellowish skin and eyes. This condition also causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting.
How to treat: You should consult your family doctor or liver specialist to assess your bilirubin levels and identify the type of hepatitis virus. This will help to guide the most appropriate treatment, which may include rest and the use of medications such as interferon, adefovir or entecavir.
Also recommended: Bilirubin: Types, Normal Ranges & What Causes High Levels tuasaude.com/en/bilirubin2. Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis can cause yellow eyes and dark urine, as well as symptoms such as white or pale stools, leg swelling, nausea or vomiting. These symptoms are especially pronounced advanced stages of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis is associated with permanent damage of the liver cells caused by alcohol abuse, fatty liver or hepatitis. Healthy cells are replaced by fibrous tissue or scarring, making the normal liver function more difficult.
How to treat: Treatment is carried out by a liver specialist and varies depending on what caused the cirrhosis. It can involve eliminating alcohol, maintaining a low fat diet or using diuretic medications to reduce swelling in the body. In its most advanced stages, the doctor may recommend a liver transplant.
3. Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system produces antibodies that attack and destroy red blood cells.
When this happens, bilirubin is released into the bloodstream causing yellow eyes as well as excessive tiredness, a swollen belly or chest pain.
How to treat: You should consult your family doctor or hematologist to start treatment, which can be done with the use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications. In more serious cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part of the spleen.
4. Gallstones
Yellow eyes from gallstones can occur when a small stone blocks the gallbladder. This prevents bilirubin from entering the intestine, and it is instead released into the blood, leading to yellow eyes.
Gallstones can also cause symptoms such as severe pain on the right side of the abdomen (especially after meals), constant diarrhea, fever, nausea or vomiting. Learn more about the symptoms of gallstones and what causes them.
How to treat: Treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist or family doctor, who may prescribe medications (e.g. ursodiol) to break-up small stones. Large stones that present with a fever and severe abdominal pain may require gallbladder removal. Check-out some natural remedies for gallstones that you can use to complement your doctor's prescribed treatment.
Also recommended: Right Side Abdominal Pain: 15 Causes, Symptoms & Treatment tuasaude.com/en/right-side-abdominal-pain5. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, which can lead to yellow eyes and intense pain on the left side of the abdomen that can radiate to the back. Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting or fever.
This pancreatic inflammation can be caused by excessive alcohol consumption, autoimmune diseases, gallstones or the use of medicines, such as liraglutide or semaglutide.
How to treat: Treatment involves hospitalization for the administration of IV fluids and medication to help manage pain.
Furthermore, it is important to make changes to your diet. The doctor will advise you to fatty foods, and and may prescribe a pancreatic enzyme supplement Learn more about the pancreatitis diet and what you should eat.
6. Neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is a very common finding in newborns, especially in premature babies. It is characterized by excess bilirubin in the bloodstream, causing yellow eyes and skin.
This condition occurs because the baby's liver is not completely formed at birth, making it difficult to eliminate bilirubin.
How to treat: Neonatal jaundice does not always require treatment. The doctor will advise you to breastfeed or bottle feed the baby every 2 hours to facilitate the elimination of intestinal waste.
However, if the jaundice worsens or if the baby has intensely yellow eyes and skin, the pediatrician may recommend phototherapy. This involves placing the baby in an incubator with direct light at all times, and only removing the baby for feeding, diaper changes and bathing.
7. Fatty liver
Fatty liver is characterized by fat cell build-up in the liver, which can be related to excessive alcohol consumption or from metabolic syndrome and being overweight.
Increased fat cells in the liver can reduce normal liver functioning, which makes it harder for the liver to filter toxins and process bilirubin. If left untreated, it can lead to an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, leading to yellow eyes.
How to treat: Fatty liver can be treated with lifestyle changes, like weight loss, a healthy diet and regular exercise. Patients with fatty liver should also eliminate alcohol intake. More severe cases may require medications and regular monitoring.
8. Malaria
Malaria is an infection caused by the Anopheles mosquito that is infected with Plasmodium protozoa. This microorganisms can grow in the liver and spread to the bloodstream, where it invades and ruptures red blood cells.
Due to the destruction of red blood cells, bilirubin is released into the bloodstream, which causes symptoms such as yellow eyes, headache, fever, sweating, chills, nausea, vomiting or weakness, for example.
How to treat: Consult your family doctor if you suspect you may have malaria. Treatment involves the use of antimalarial drugs such as chloroquine, primaquine or mefloquin.
9. Pinguecula
Pinguecula is a breakdown of conjunctival tissue in the eye. It occurs due to the overgrowth of tissue and is made up of proteins, fat and calcium. This tissue is associated with a yellow color.
Pinguecula can give the eye a yellow tinge, and can cause other symptoms such as dry eyes, eye irritation, swelling, redness, blurry vision and itching.
How to treat You should consult an ophthalmologist to confirm a diagnosis and begin appropriate treatment. This can be done with the use of eye drops and ointments. In some cases, surgery may also be recommended.
10. Medication side effect
Some medications can cause serious harm to the liver, especially if taken for doses much higher than prescribed or if taken for longer than recommended.
Medications that can lead to yellowing of the eyes secondary to liver cancer include high doses of acetaminophen, some antibiotics or even anabolic steroids.
How to treat: If you start to notice yellow eyes after starting a new medication, you should inform your prescriber or pharmacist immediately. Your doctor will likely assess your liver functioning and determine whether the medication should be stopped or substituted. Do not discontinue the medication on your own without speaking to your prescriber or pharmacist first.
11. Liver cancer
Liver cancer is associated with a malignant tumor that may not present with any symptoms in its early stages.
However, as the disease progresses, symptoms such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, abdominal pain, weight loss or abdominal swelling may appear.
Also recommended: 11 Liver Disease Symptoms (Online Symptom Quiz) tuasaude.com/en/liver-disease-symptomsHow to treat: The treatment is oriented out by an oncologist, who may recommend surgery to remove the tumor, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy or a liver transplant.





























